Nasopalatine Duct Cyst Treatment
Nasopalatine duct cyst treatment. The objective of this article is to report a case of NPDC in which different imaging means were used for diagnosis treatment and postoperative follow-up of the lesion. Surgical enucleation of the cyst is performed under local anesthesia and the result is generally positive when the cyst is aspirated before removal. Transnasal endoscopic marsupialization can also be applied.
We enucleated all cysts under local anesthesia Figures 67. However it is not uncommon to see evidence of endodontic therapy because the nasopalatine duct cyst was previously clinically misdiagnosedas a periapical cyst or granuloma. If the cyst shows signs of infection or shows progressive enlargement then surgical intervention may be warranted.
Incisive canal cyst or nasopalatine duct cysts NPDCs are the most common non-odontogenic and developmental cysts of the maxilla. Nasopalatine duct cyst treatment. Cystectomy and fenestration surgery of the nasal cavity may is an option for treatment of huge maxillary cysts such as NPDC in the midline.
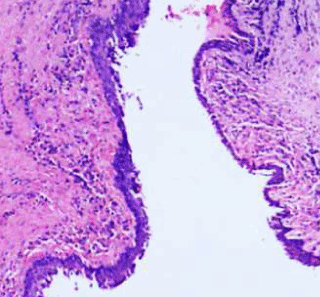
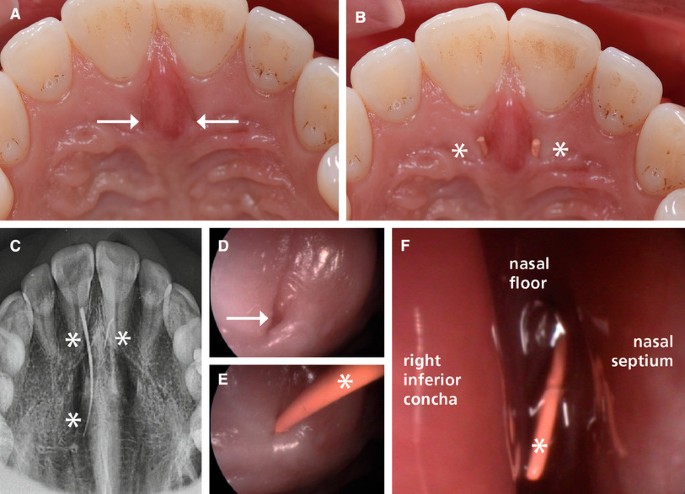
Demonstration of the removal of a nasopalatine canal cyst. Incisive canal cysts also known as nasopalatine duct cysts NPDC are developmental non-neoplastic cysts arising from degeneration of nasopalatine ducts. The persistence of ductal epithelium leads to formation of cyst.
Recurrence is uncommon having been reported in 0-11 of patients 45. These ducts usually regress in fetal life. A cone-beam computed tomography CBCT is a valuable tool.
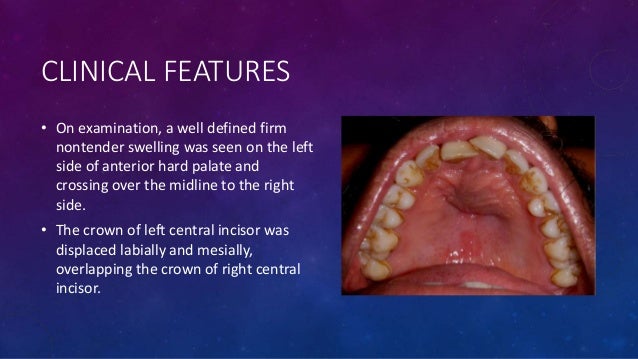
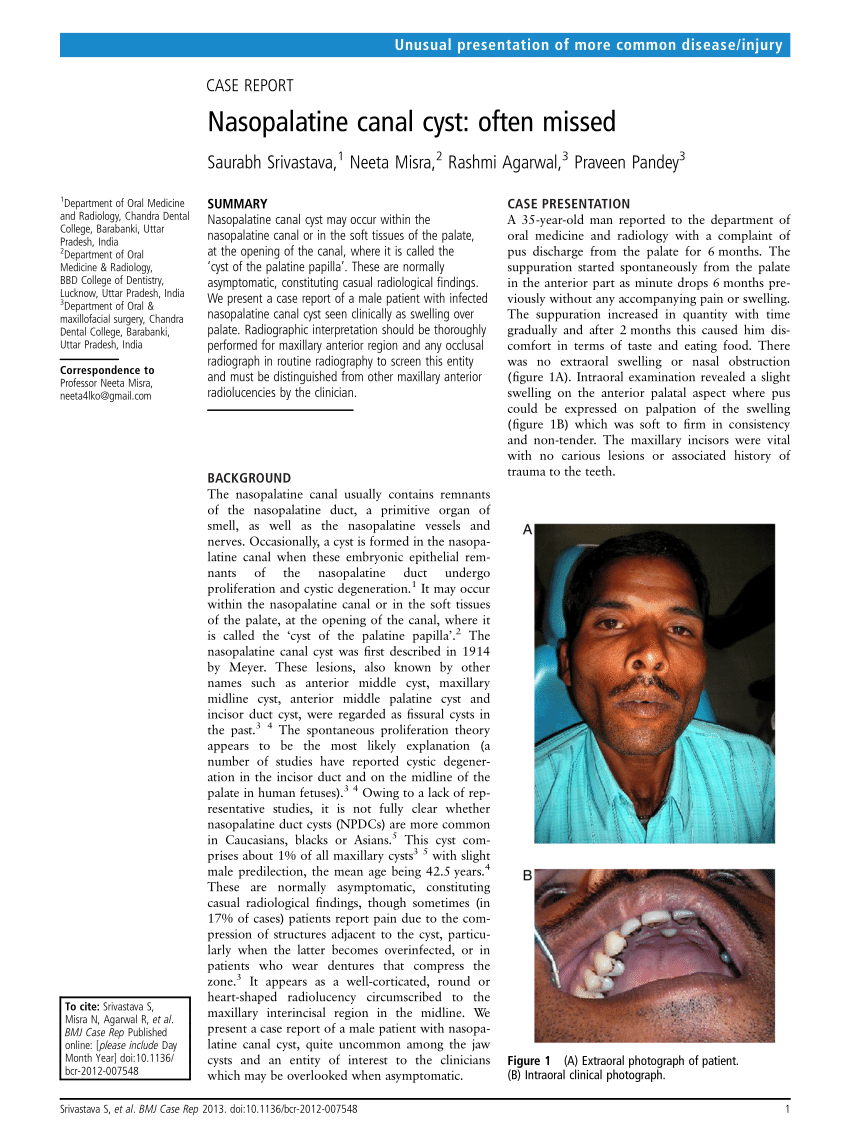
Abstract The nasopalatine duct cyst NPDC is the most common non-odontogenic epithelial cyst occurring in the maxilla and it arises from the epithelial remnants of the nasopalatine duct. This elderly denture wearing patient had a swelling in the mid line of the hard palate and was diagnosed as a rare nasopalatine duct cyst histo pathologica. Nasopalatine duct cysts are treated by enucleation via a palatine or buccal approach.
By means of the clinical and radiographic aspects the initial diagnosis was nasopalatine duct cyst in which the first line treatment is usually surgical enucleation after consideration of. Nasopalatine duct cyst presents in the fourth to sixth decades of life with a male predilection.
Incisive canal cyst or nasopalatine duct cysts NPDCs are the most common non-odontogenic and developmental cysts of the maxilla.
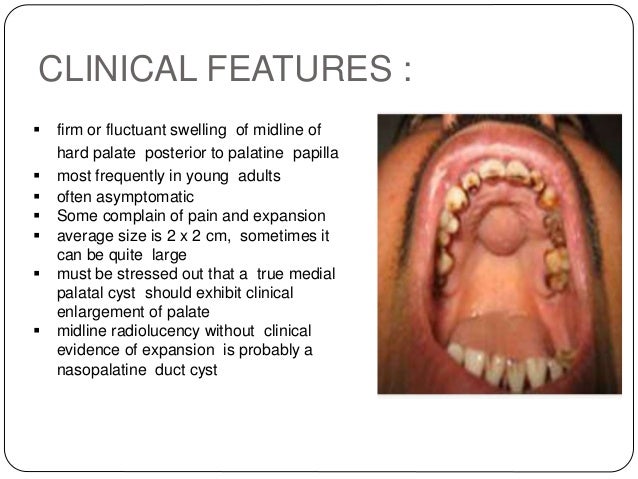
These developmental NPDC are usually asymptomatic and are discovered during routine radiological examination done for some other diagnosis. Incisive canal cysts also known as nasopalatine duct cysts NPDC are developmental non-neoplastic cysts arising from degeneration of nasopalatine ducts. Cystectomy and fenestration surgery of the nasal cavity may is an option for treatment of huge maxillary cysts such as NPDC in the midline. Nasopalatine duct cyst treatment. Of a previously asymptomatic nasopalatine duct cysts and consist primarily of swelling drainage and pain. A cone-beam computed tomography CBCT is a valuable tool. Surgical treatment consisted of enucleation in the first case and marsupialization in the second case. These ducts usually regress in fetal life. Nasopalatine duct cysts are treated by enucleation via a palatine or buccal approach.
Incisive canal cysts also known as nasopalatine duct cysts NPDC are developmental non-neoplastic cysts arising from degeneration of nasopalatine ducts. Incisive canal cyst or nasopalatine duct cysts NPDCs are the most common non-odontogenic and developmental cysts of the maxilla. These developmental NPDC are usually asymptomatic and are discovered during routine radiological examination done for some other diagnosis. Nasopalatine duct cyst treatment. Surgical treatment consisted of enucleation in the first case and marsupialization in the second case. Nasopalatine duct cysts are usually treated by enucleation through the palatinal approach. Surgical enucleation of the cyst is performed under local anesthesia and the result is generally positive when the cyst is aspirated before removal.





























Post a Comment for "Nasopalatine Duct Cyst Treatment"