Acute Chest Syndrome Pathophysiology
Acute chest syndrome pathophysiology. Acute coronary syndrome is a term for a group of conditions that suddenly stop or severely reduce blood from flowing to the heart muscle. Causes may include sepsis pancreatitis. Common predisposing clinical conditions include sepsis pneumonia severe traumatic injury and aspiration of gastric contents.
When blood cannot flow to the heart muscle the heart muscle can become damaged. Acute chest pain can be caused by an extensive variety of disorders ranging from life-threatening syndromes such as ACSs acute aortic diseases and PE to conditions that are relatively harmless. Pediatr Clin North Am.
Health policy and cost issues related to the care of patients with cardiac or pulmonary disorders or the care of acutely or critically ill patients. Acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath dyspnea rapid breathing tachypnea and bluish skin coloration cyanosis.
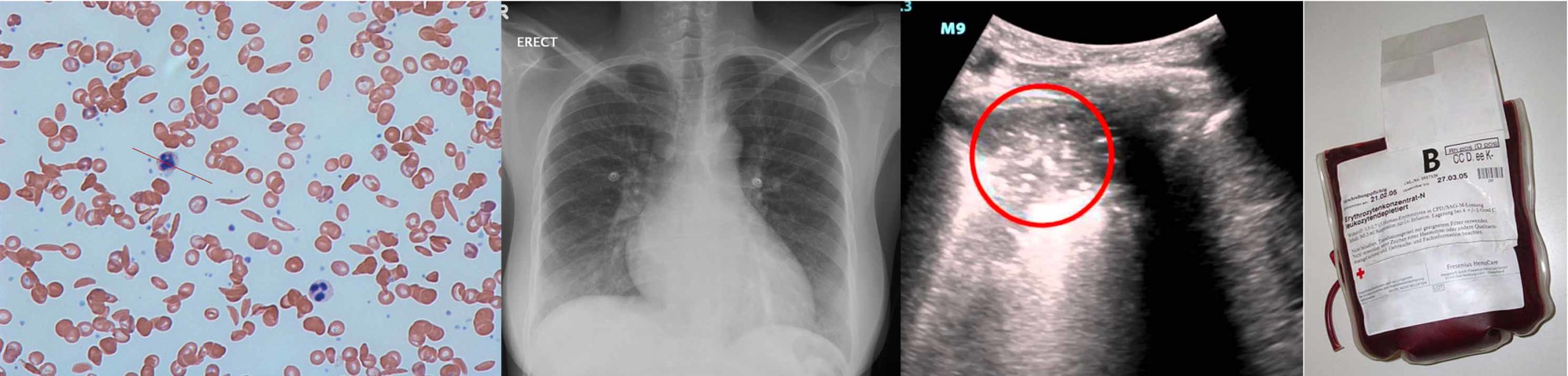
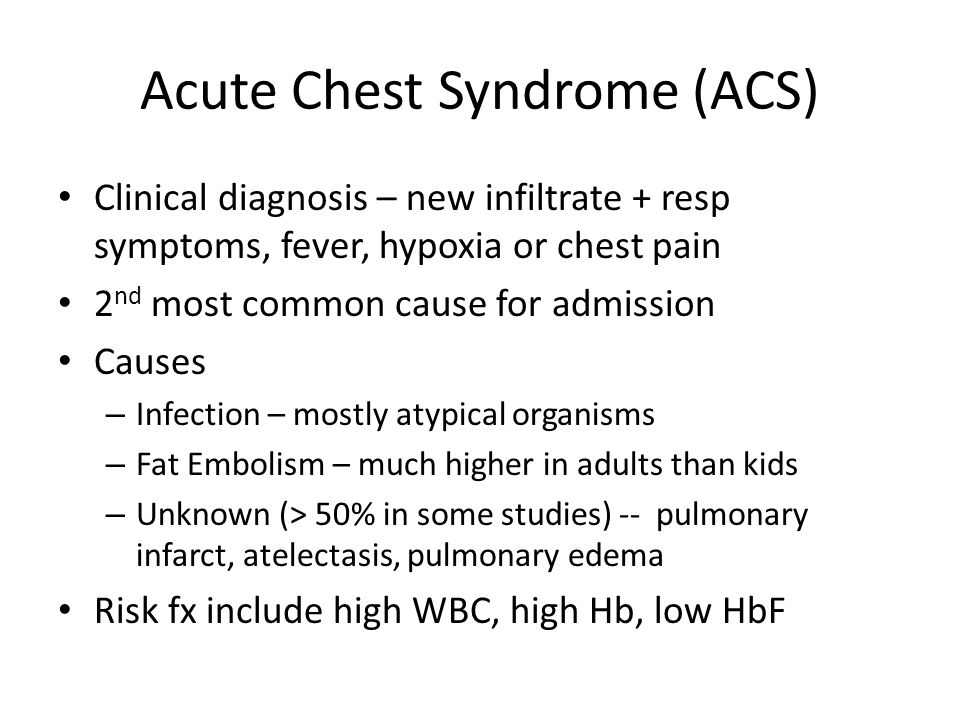
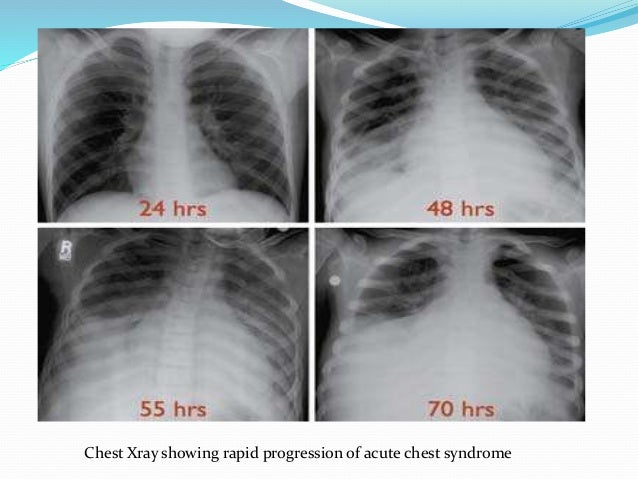
Image shows endotracheal tube left subclavian central venous catheter in superior vena cava and bilateral patchy opacities in mostly middle and lower lung zones. 2 Fever andor respiratory symptoms eg cough dyspnea or chest pain. Acute chest syndrome is a clinical syndrome which is defined as the combination of.
Care of patients with acute or chronic cardiac or pulmonary disorders across the lifespan. The acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS is a syndrome of acute respiratory failure characterized by the acute onset of non-cardiogenic pulmonary oedema due to increased lung endothelial and alveolar epithelial permeability. Anteroposterior portable chest radiograph in patient who had been in respiratory failure for 1 week with diagnosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome.
This is an intentionally broad definition which doesnt exclude other diagnoses. Hepatorenal syndrome is diagnosed when kidney function is reduced but evidence of intrinsic kidney disease such as hematuria proteinuria or abnormal kidney ultrasonography. Heart attack and unstable angina are both acute coronary syndromes ACS.
4 7 It must be emphasised that there are important gender differences in epidemiology pathophysiology clinical presentation response to therapy. Acute heart failure AHF is a relevant public health problem causing the majority of unplanned hospital admissions in patients aged of 65 years or more.
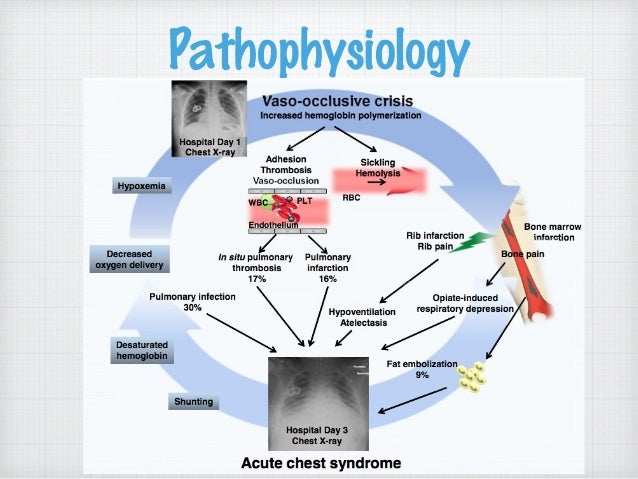
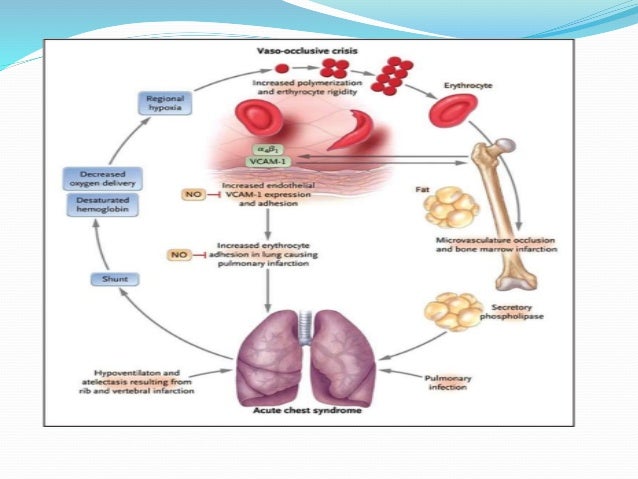
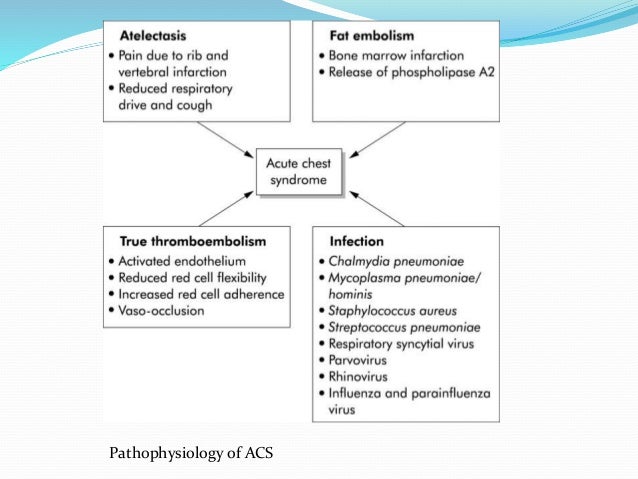
Acute chest syndrome is a clinical syndrome which is defined as the combination of.
The arrival of emboli into the pulmonary circulation can induce acute pulmonary hypertension and acute right heart overload which could potentially result in right ventricular failure and in some patients right ventricular infarction This condition is diagnosed at autopsy in 60 of patients who die of a pulmonary embolism. This is an intentionally broad definition which doesnt exclude other diagnoses. By continuing to browse this site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 SARS-CoV-2 is the pathogen responsible for the coronavirus disease 2019 COVID-19 pandemic which has resulted in global healthcare crises and. Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema is a disease process that results in acute hypoxia secondary to a rapid deterioration in respiratory status. Image shows endotracheal tube left subclavian central venous catheter in superior vena cava and bilateral patchy opacities in mostly middle and lower lung zones. Acute tubular necrosis ATN is the most common cause of acute kidney injury AKI in the renal category. Hepatorenal syndrome HRS the extreme manifestation of renal impairment in patients with cirrhosis is characterized by reduction in renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate. Acute chest syndrome is a clinical syndrome which is defined as the combination of.
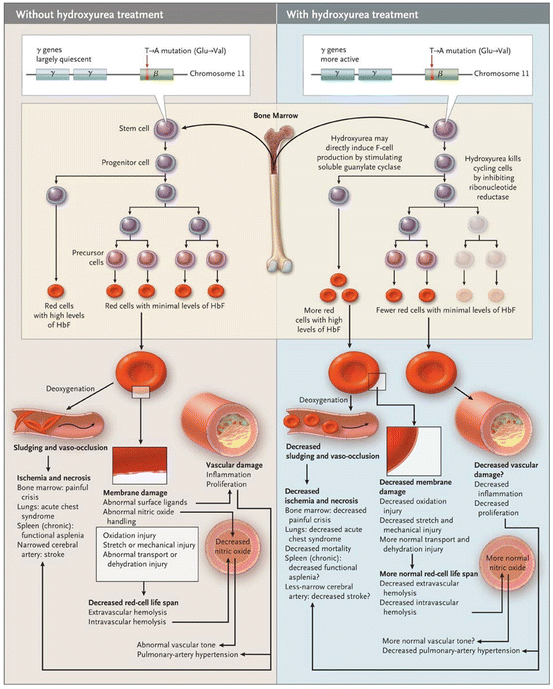
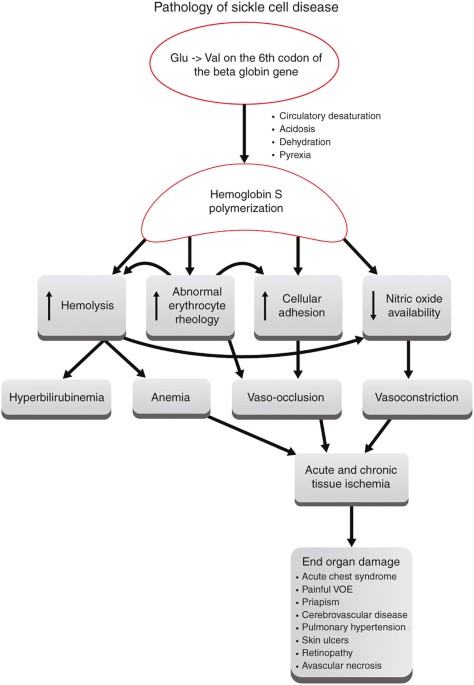
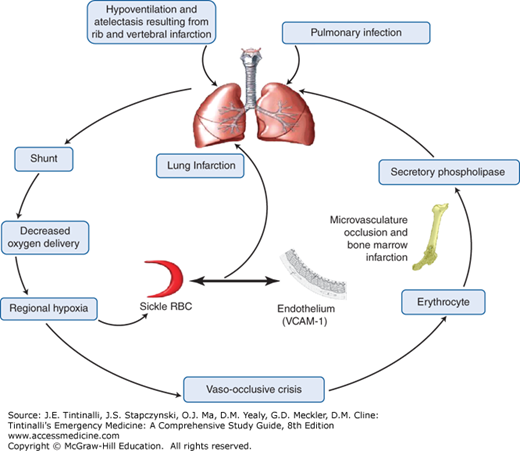
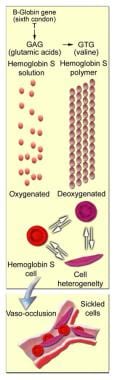
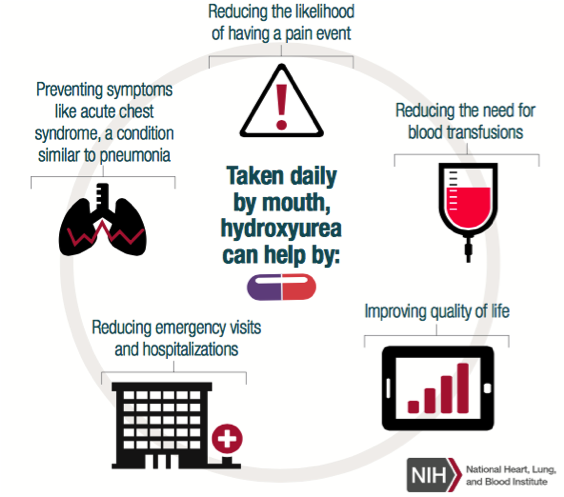
Causes may include sepsis pancreatitis. Acute chest syndrome refers to a spectrum of disease from a mild pneumonic illness to acute respiratory distress syndrome and multi-organ failure. Care of acutely ill critically ill and chronically ill patients across the lifespan. The arrival of emboli into the pulmonary circulation can induce acute pulmonary hypertension and acute right heart overload which could potentially result in right ventricular failure and in some patients right ventricular infarction This condition is diagnosed at autopsy in 60 of patients who die of a pulmonary embolism. The initial insult which may be pulmonary infection fat embolism andor pulmonary infarction causes a fall in alveolar oxygenation tension which causes HbS polymerization. Recognizing and promptly treating ARDS is critical to reduce the associated high mortality. Acute tubular necrosis ATN is the most common cause of acute kidney injury AKI in the renal category.



























Post a Comment for "Acute Chest Syndrome Pathophysiology"