Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Case Study
Acute respiratory distress syndrome case study. Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome The pt continues to experience severe respiratory distress and is given an entraintment device wan FiO2 of 60. The most common cause of death from COVID-19 is acute respiratory failure. Despite the utilization of conventional medical treatments and optimum respiratory support modalities the patients condition worsened and death was imminent without salvage therapy.
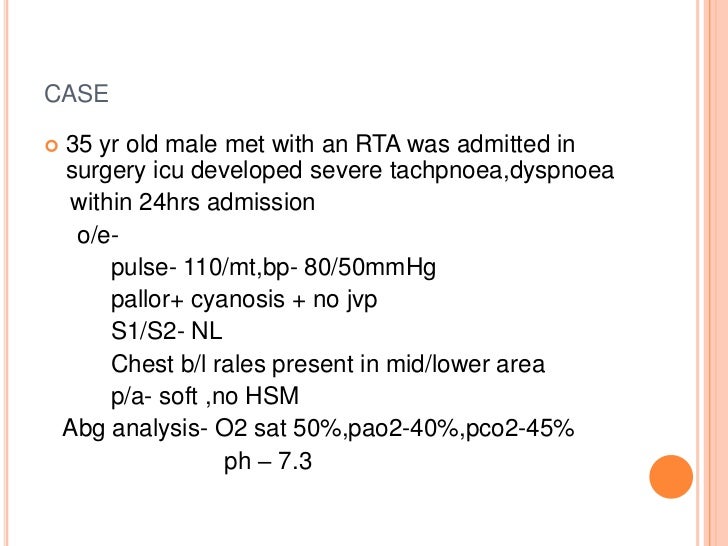
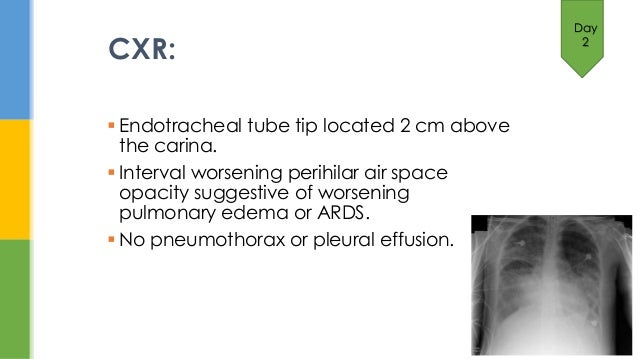
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDS Case Study Rocky is a 56-year-old aeronautical scientist who was involved in a motor vehicle crash MVC. We report the case of a 78-year-old female with a history of hypertension cerebrovascular accident CVA type 2 diabetes mellitus and sarcoidosis who presented to the emergency department with. Note the endotracheal tube ETT nasogastric tube NGT and two central lines right internal jugular RIJV and right subclavian RSCV.
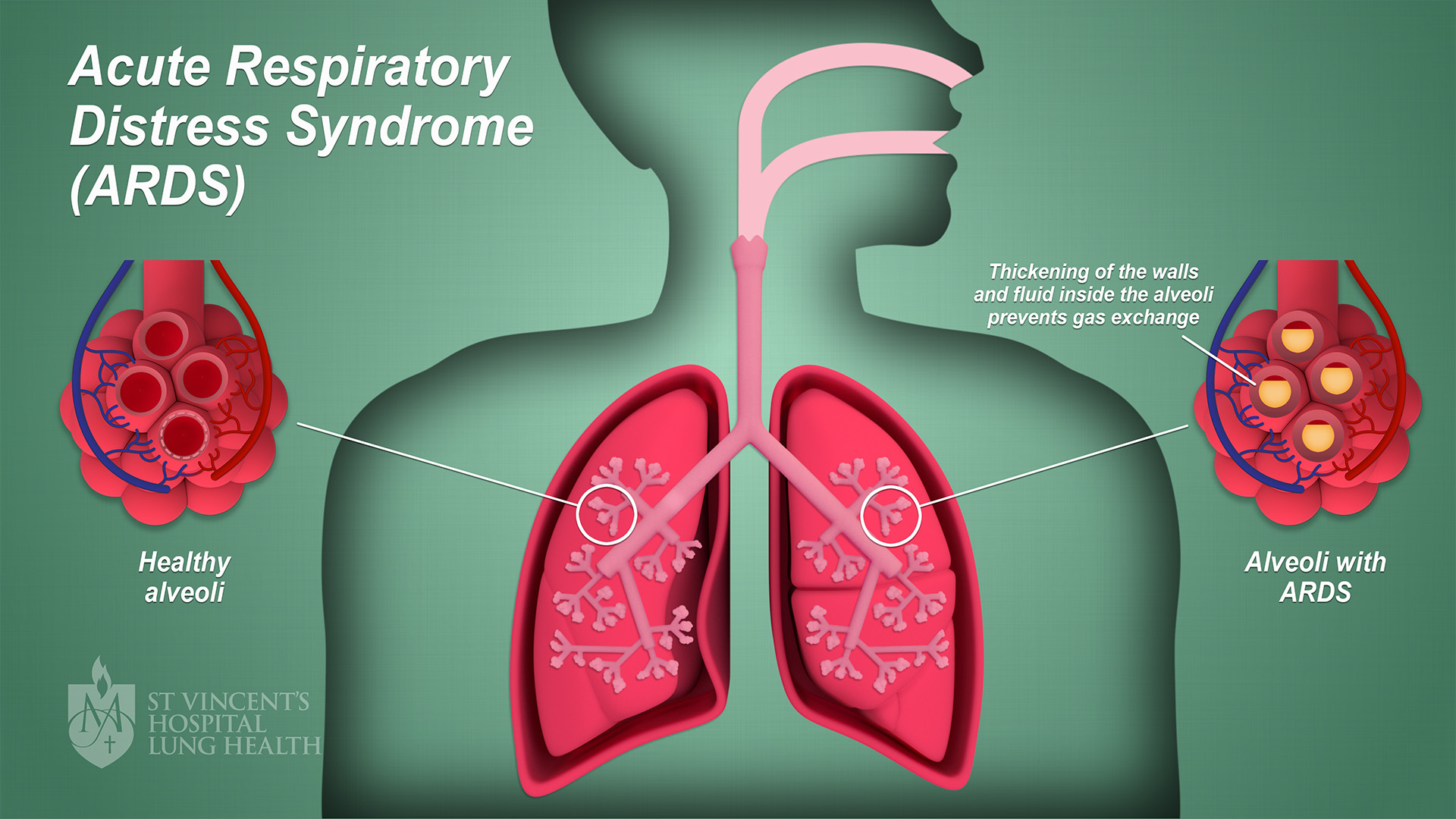
Acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS chest x-ray This 37-year-old man developed severe acute pancreatitis and required ICU admission. Also known as Acute Lung Injury ARDS Noncardiac Pulmonary Edema Acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS is a serious lung condition that causes low blood oxygen. Acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS is a condition of dysfunctional gas exchange ie pulmonary interstitial and alveolar edema progressing to advanced fibrosis that is characterized by acute onset bilateral pulmonary infiltrates severe hypoxia the absence of evidence of left atrial hypertension and a significant risk of mortality25.
Despite the utilization of. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDS Sudden progressive form of acute respiratory failure Alveolar capillary membrane becomes damaged and more permeable to intravascular fluid. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema or upperlower airway obstruction ie.
Agarwal R Reddy C Aggarwal AN et al. Bacterial or viral pneumonia acute exacerbations of chronic respiratory conditions ie. Identify the pathology and etiology of ARDS.
Is there a role for noninvasive ventilation in acute respiratory distress. People who develop ARDS are usually ill due to another disease or a major injury. This case study explores the management of an unusually complicated case of acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS extending over 52 days of hospitalization.
Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. This case study explores the management of an unusually complicated case of acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS extending over 52 days of hospitalization.
Upon completion of this activity participants should be able to.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS is a condition of dysfunctional gas exchange ie pulmonary interstitial and alveolar edema progressing to advanced fibrosis that is characterized by acute onset bilateral pulmonary infiltrates severe hypoxia the absence of evidence of left atrial hypertension and a significant risk of mortality25. Also known as Acute Lung Injury ARDS Noncardiac Pulmonary Edema Acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS is a serious lung condition that causes low blood oxygen. Bacterial or viral pneumonia acute exacerbations of chronic respiratory conditions ie. Acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS is a condition of dysfunctional gas exchange ie pulmonary interstitial and alveolar edema progressing to advanced fibrosis that is characterized by acute onset bilateral pulmonary infiltrates severe hypoxia the absence of evidence of left atrial hypertension and a significant risk of mortality25. This case study explores the management of an unusually complicated case of acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS extending over 52 days of hospitalization. Agarwal R Reddy C Aggarwal AN et al. Identify the pathology and etiology of ARDS. Despite the utilization of conventional medical treatments and optimum respiratory support modalities the patients condition worsened and death was imminent without salvage therapy. As of April 2020 the coronavirus 2019 COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in more than 210000 deaths globally.
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDS Sudden progressive form of acute respiratory failure Alveolar capillary membrane becomes damaged and more permeable to intravascular fluid. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Respiratory distress syndrome RDS which is presented by higher respiratory rate than normal range for age and other clinical symptoms and signs including grunting nasal flaring retraction and cyanosis have a variety of causes in newborn infants and other pediatrics. The acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS was initially defined in 1967 with a case-based report that described the clinical presentation in critically ill adults and children of acute hypoxaemia noncardiogenic pulmonary oedema reduced lung compliance increased lung stiffness increased work of breathing and the need for positive-pressure ventilation in association. COPD asthma congestive heart failure ie. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema or upperlower airway obstruction ie. He was the driver of a vehicle that was hit head-on pinning him behind the steering wheel.





































Post a Comment for "Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Case Study"